|
Chronic
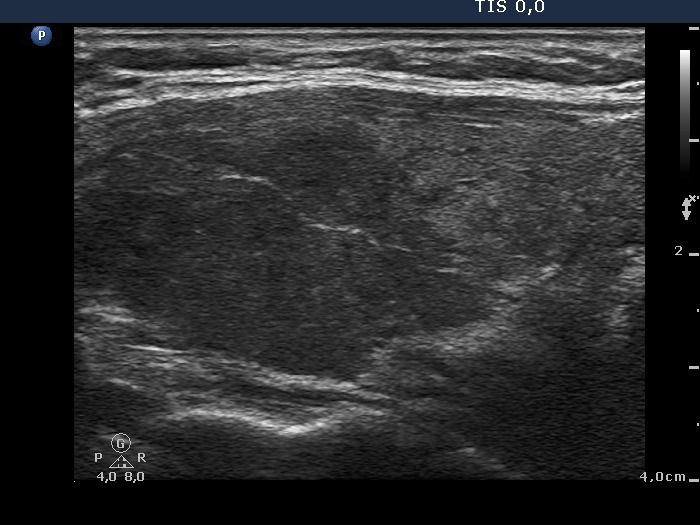
lymphocytic thyroiditis - Figure 2. Focal hypoechogenic areas.
Hypoechogenic areas within echonormal or minimally hypoechogenic background - this is most common sonographic presentation of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. The correct interpretation of this pattern is the essence of thyroid ultrasonography. The most important properties in the differentiation of thyroiditis and a nodule in pathological sense are the following: the basic echpattern, the sum, the size and the borders of the hypoechogenic lesions and the consideration of clinical and biochemical data. A clear distinction is possible in around 80% of such patterns. |
CLOSE |